Intro to GlucoPy#
Using GlucoPy is simple. The first step is to import the package.
import glucopy as gp
Then, you need to import CGM data.
Importing data#
Using the
read_csv()function:
gf = gp.read_csv('path_to_file.csv')
Using the
read_excel()function:
gf = gp.read_excel('path_to_file.xlsx')
Using a
pandas.DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('path_to_file.csv')
gf = gp.Gframe(df)
If you have no CGM dataset, you can still try this toolbox using the sample data provided with the package in the
data()function
gf = gp.data()
All the previous functions return an instance of Gframe which is the main object of the package. This object
contains the CGM data and provides a set of methods to manipulate and analyze it.
Calculating metrics#
Basic metrics#
The Gframe object provides a set of methods to calculate metrics from the CGM data. For example, simple metrics like
the mean, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation can be calculated using like this:
In [1]: import glucopy as gp
In [2]: gf = gp.data()
In [3]: mean = gf.mean()
In [4]: std = gf.std()
In [5]: cv = gf.cv()
In [6]: mean, std, cv
Out[6]: (144.28068149003755, 64.72869948664865, 0.44863039748753963)
Calculating metrics for each day#
Most of the methods provided by Gframe can be calculated for each day of the dataset. For example, to calculate the
mean for each day:
In [7]: day_means = gf.mean(per_day=True)
In [8]: day_means
Out[8]:
Day
2020-11-27 277.636364
2020-11-28 138.677083
2020-11-29 146.552083
2020-11-30 120.052083
2020-12-01 139.229167
...
2021-03-14 146.645161
2021-03-15 126.593407
2021-03-16 161.957895
2021-03-17 113.833333
2021-03-18 170.000000
Name: Mean, Length: 112, dtype: float64
And since the returned value when per_day is set to True is a pandas.Series, you can use any method provided
by the pandas.Series object. For example, to calculate the max of the means:
In [9]: day_means.max()
Out[9]: 277.6363636363636
You can alos access the mean of a specific day using the index of the pandas.Series:
In [10]: day_means["2020-12-01"]
Out[10]: 139.22916666666666
Glycaemia specific metrics#
Gframe also provides methods to calculate metrics specific to glycaemia. For example, to calculate the
Time in Range (TIR) for a given range:
In [11]: tir = gf.tir() # default range is [70, 180]
In [12]: tir
Out[12]:
ranges
(0.0, 70.0] 11.24
(70.0, 180.0] 61.04
(180.0, 445.0] 27.72
Name: Time in Range, dtype: float64
Calculating the Mean of Daily Differences (MODD)
In [13]: modd = gf.modd()
In [14]: modd
Out[14]: 69.06133828996282
Calculating the Glucose Variability Percentage (GVP)
In [15]: gvp = gf.gvp()
In [16]: gvp
Out[16]: 33.76052564549197
You can check the documentation of Gframe to see the full list of methods provided.
Summary#
You can also calculate a summary of the dataset using the Gframe.summary() method:
In [17]: summary = gf.summary()
In [18]: summary
Out[18]:
Metric Value
0 Mean 144.28
1 Standard Deviation 64.73
2 Coefficient of Variation 0.45
3 IQR 95.00
4 MODD 69.06
5 % Time below 70 [mg/dL] 11.24
6 % Time in between (70,180] [mg/dL] 61.04
7 % Time above 180 [mg/dL] 27.72
8 AUC 23075053.50
9 MAGE 121.68
10 Distance Traveled 115800.00
11 LBGI 5.74
12 HBGI 13.51
13 ADRR 101.97
14 GRADE Hypoglycaemia % 16.00
15 GRADE Euglycaemia % 8.05
16 GRADE Hyperglycaemia % 75.95
17 Q-Score 13.89
18 CONGA 45.72
19 GVP 33.76
20 MAG 43.56
21 DFA 0.85
22 SampEn 0.63
23 MSE 1.26
Plotting#
GlucoPy uses Plotly to create interactive plots. The module Plot provides a set of functions to create different
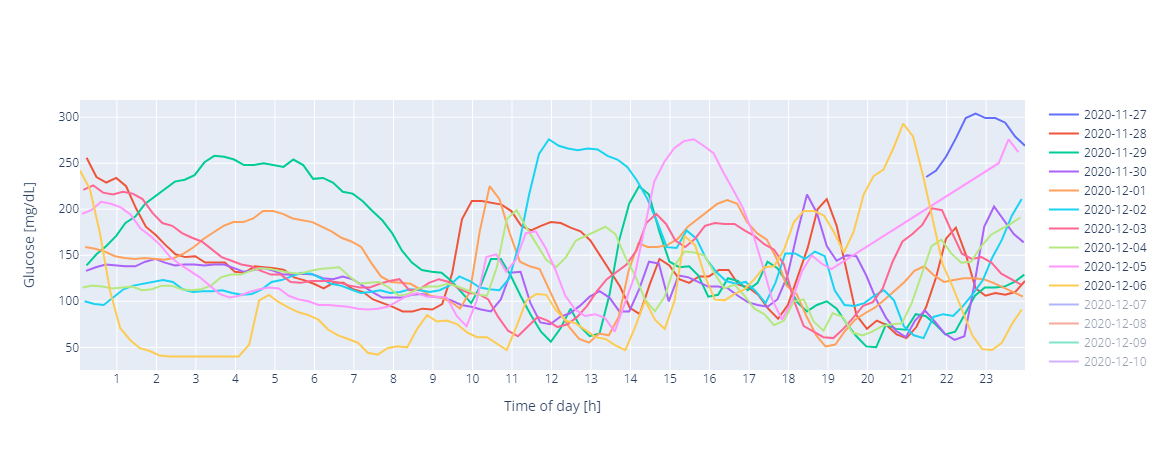
types of plots. For example, to create a plot of the CGM data:
In [19]: gp.plot.per_day(gf,num_days=7)
Out[19]:
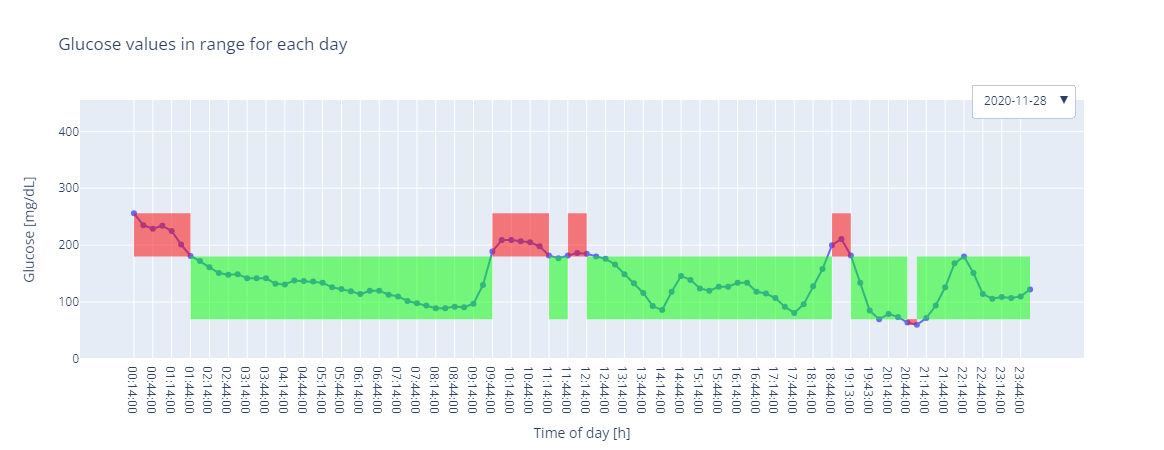
Or a plot that highlighs the TIR:
In [20]: gp.plot.tir(gf)
Out[20]: